Audio inductor
Application background: audio amplifier
The audio amplifier used in the speaker is divided into Classes A, B, AB and D. Among them, class A, B and AB amplifiers will lose power and generate a lot of heat loss due to the linear operation of bias components and output transistors. In modern times, they require portability, lightness and energy saving. Under the premise of low power consumption and high performance, it is gradually replaced by class D amplifiers with low power consumption and high performance.
performance advantages. because The transistor in a Class D amplifier only acts as a switch to control the flow of current through the load, so the power loss caused by the output stage is minimal. because The requirements for heat sinks of Class D amplifiers can be greatly reduced or eliminated, so they are very suitable for compact high-power applications. The following figure is the application block diagram of a Class D amplifier:

Class D Amplifier (Class D)
Class D amplifiers were developed in the 1950s. From the early days, they had problems such as high distortion and thin sound. After ten years of research and improvement and the evolution of digital circuits, Class D amplifier circuits currently have the advantages of low power consumption, small size, low distortion and easy tuning, and have been widely used in home audio, car audio, audio-visual theaters, etc. usage environment.
TRIO's audio inductor series products are designed for the back-end low-pass filter of Class D amplifier circuits. The entire series of products have passed the automotive AEC-Q200 certification provides system developers with high-quality products with complete specifications, high reliability and low noise ratio.
Audio inductor applicationClass D amplifier circuits can be divided into Half Bridge and Full Bridge Line architecture. The output stages of both lines need to be filtered through low-loss low-pass filters. The following figure is the basic structure of a class D amplifier. Most audio signals are not pulse type (PWM), so they need to be filtered through A modulator converts audio input into a pulse signal. The frequency component of the pulse includes the basic audio signal and the high-frequency energy generated by the modulation process. The high-frequency energy is usually accompanied by high electromagnetic interference (EMI), so we will insert a low-pass between the output stage and the speaker. filters to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI).
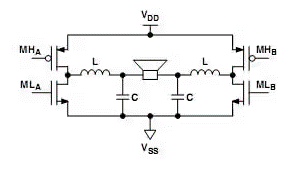
LC filter Design of Inductor
The purpose of filter design selection is to reduce the filter response at the highest audio frequency required Minimize to obtain lowest bandwidth. For common speaker impedances and standard L and C values, refer to Figure 2 to provide standard component values and their corresponding bandwidth responses, in which the speaker resistance (speaker resistance) reference uses common impedance values 4, 6 and 8Ω. .
Advantages of TRIO audio inductors
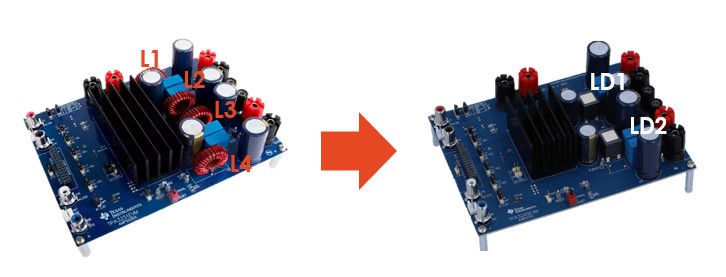
The traditional LC filter inductor selection is mainly toroidal inductor that is easy to make and low cost, but its existence There are many problems, such as poor EMI performance, LC resonance noise problem, high loss and low efficiency, and the inability to be fully SMD. TRIO has launched an integrated dual audio inductor product to perfectly replace the traditional solution.
The one-piece inductor type has the advantages of high yield, high reliability and high durability due to its fully automated process. In addition, due to its closed magnetic circuit design, it has greatly improved EMI and anti-SNR performance. In addition, it adopts back-to-back The dual inductor process has the same EVB size as shown in the figure below, but its design volume is reduced by nearly 40%. The traditional toroidal inductor requires space for a total of four inductors L1~L4, while the new inductor design is reduced to only the space of LD1 and LD2 , which can significantly reduce the space pressure caused by mechanical limitations. In addition, the back-to-back dual inductor process also brings high electrical characteristics consistency, which makes it easier for developers to match and adjust the left and right audio channels.